Chicks born without a shell 🐣 How is this possible?
Published by Cédric,
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: Nature Scientific Reports
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: Nature Scientific Reports
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
In this approach, researchers place a chicken embryo, without its shell, in a transparent box where it is held by a thin protective vitelline membrane. This technique overcomes the major challenge encountered so far: observing the embryo without having to break the shell, which risked compromising its development.
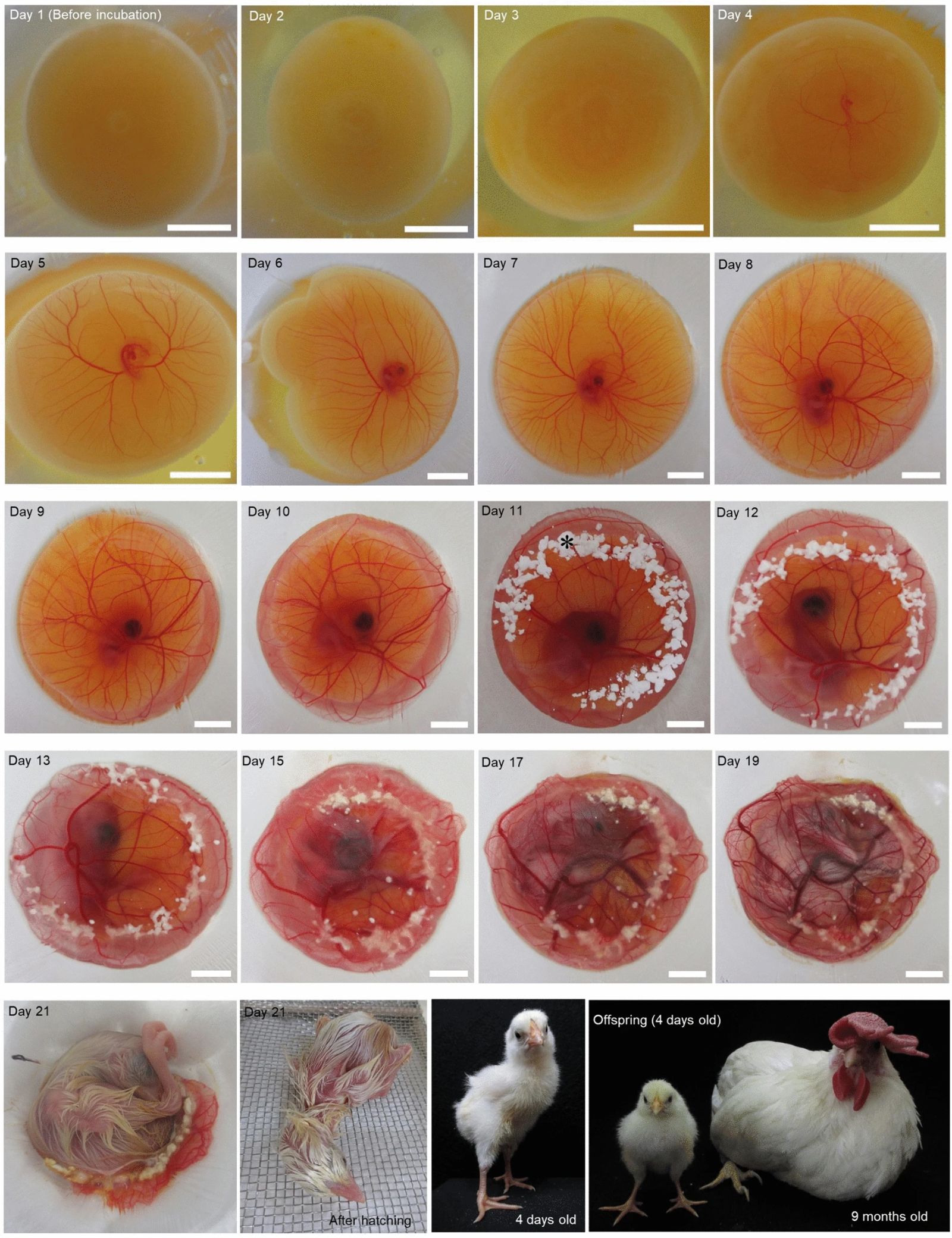
Visible embryonic development and hatched chicks (4 days old and 9 months old). The embryonic development sequence is shown in visible culture, from the blastoderm stage to hatching. The photograph for the 10th day of incubation was taken before the application of calcium carbonate powder. Scale bar, 0.39 inches (1 cm).
*Calcium carbonate powder.
Thus, a transparent film placed over the box facilitates continuous observation. Thanks to an agitator, the system prevents the membrane from drying out, offering a stable growth environment for the embryo. The controlled stirring is carried out at a precise angle of seven degrees. This regular rotation ensures an optimal supply of moisture, indispensable for the proper development of the embryo.
At the end of 21 days, the first healthy chicks emerged. This novel process preserves the embryo until hatching, a result previously impossible to achieve. Beyond the mere technical feat, this method allows for unprecedented observation. Researchers hope to learn more about stem cell development in the embryo.
Stem cells, valuable for medicine, are the foundation of blood cells. Studying them could help combat severe diseases such as leukemia or Cooley's anemia.
Thanks to this method, tests on toxic agents are also conceivable. It could additionally open up new avenues for research in toxicology and developmental biology.
What is a stem cell?
Stem cells are "immature" cells possessing the unique ability to transform into different cell types. They can differentiate into red blood cells, white blood cells, nerve cells, or other specific cell types based on the body's needs.
Present in embryos and certain adult tissues, stem cells play a critical role in the growth and repair of the organism. In adults, they are found in areas like the bone marrow, where they contribute to blood renewal.
In medical research, stem cells are essential for understanding cellular regeneration and treating certain diseases. They open up possibilities for regenerating damaged tissues and better understanding pathologies such as cancers or degenerative diseases.
Why study chicken embryos?
The chicken embryo is a unique research model. Its rapid growth and accessible structure allow scientists to study cellular development in real time, while limiting the ethical constraints often associated with mammalian models.
Moreover, the embryonic development of chickens shares many similarities with that of mammals. By observing its formation stages, researchers can discover mechanisms common to many organisms, thus offering insights for regenerative medicine and stem cell research.
Experiments on chicken embryos also allow for testing the effects of chemicals or experimental conditions on the cells. This approach contributes to evaluating the toxicity of new compounds and better understanding the mechanisms of cellular mutation.