At 18, he discovers 1.5 million unknown celestial objects with his AI algorithm 🌟
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
Matteo Paz developed an innovative method to process data from NASA's NEOWISE telescope. His work, published in The Astronomical Journal, enables the identification of variable objects like quasars or exploding stars with unprecedented accuracy.

Matteo Paz with Caltech president Thomas F. Rosenbaum.
Credit: California Institute of Technology
The summer of 2022 was decisive for Matteo Paz, who joined the Caltech Planet Finder Academy. Under the guidance of Professor Andrew Howard and mentor Davy Kirkpatrick, he was able to bring his project to life. Kirkpatrick, inspired by his own mentor, saw exceptional potential in Matteo Paz and encouraged him to pursue his ambitions.
NEOWISE, originally designed to track asteroids, has accumulated a wealth of data on variable celestial objects. Paz chose not to analyze this information manually but instead created an AI model capable of doing so. His approach enabled the efficient processing of nearly 200 billion detections.
With the help of Caltech scientists, Matteo Paz refined his algorithm to recognize subtle patterns in infrared data. This collaboration led to the detection of 1.5 million potential objects, opening new perspectives for astronomy. The complete catalog of these discoveries will be published in 2025.
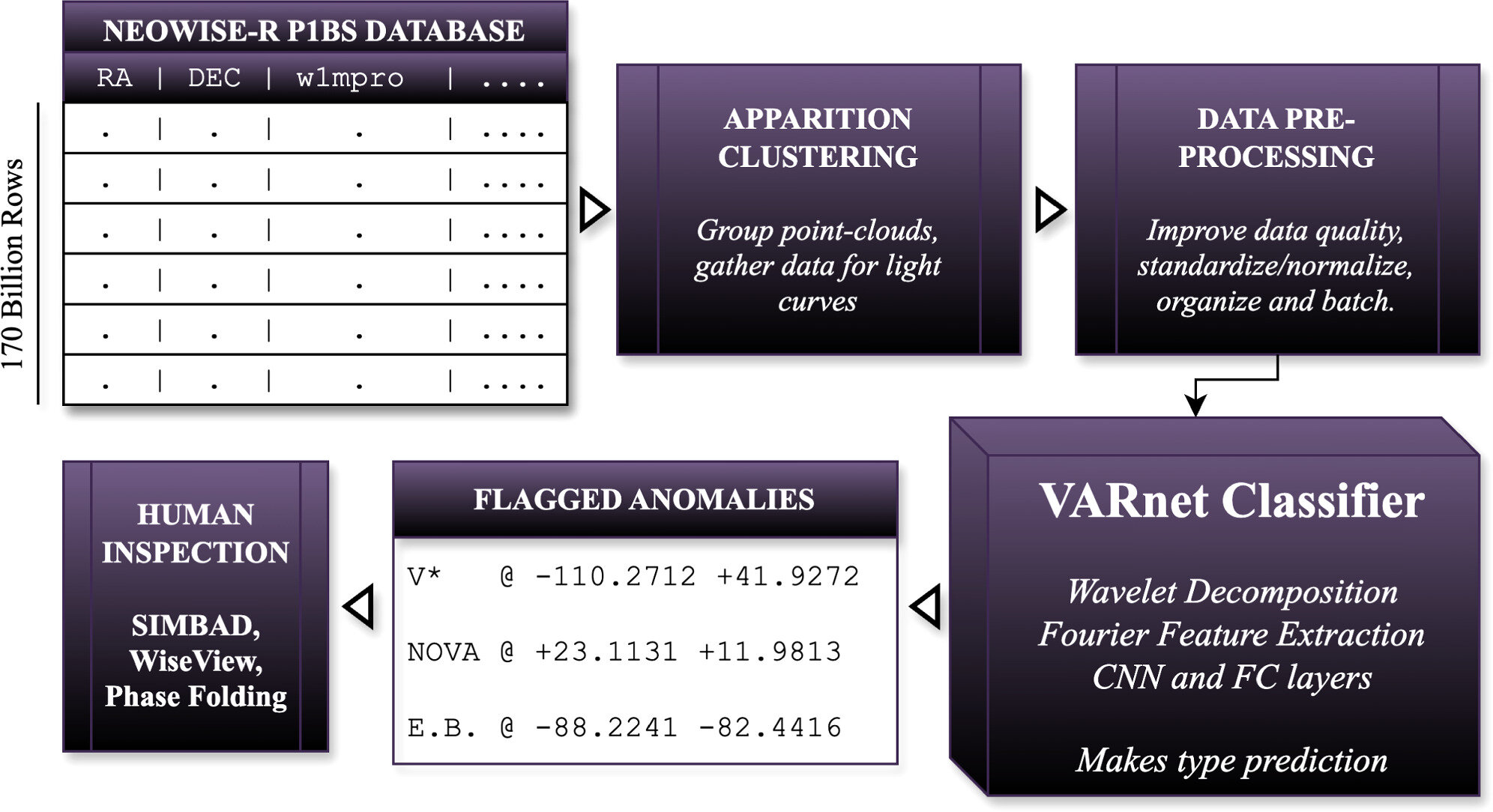
The anomaly extraction pipeline.
Credit: The Astronomical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ad7fe6
Matteo Paz is already considering other applications for his model, such as stock market analysis or atmospheric variation studies. His work at Caltech, where he is now employed, reflects his dedication and early talent for scientific research.
How does Matteo Paz's AI algorithm work?
Matteo Paz's algorithm uses machine learning techniques to analyze temporal data from the NEOWISE telescope. It is designed to detect minute variations in the brightness of celestial objects, enabling the identification of phenomena like quasars or variable stars.
The model relies on Fourier and wavelet methods to extract variable candidates from billions of data points. This approach is particularly effective for processing vast sets of astronomical data.
Matteo Paz trained his algorithm on well-organized and complete data, maximizing its accuracy. The success of this method paves the way for its application in other fields requiring time-series analysis.
What is the NEOWISE telescope and why is it important?
NEOWISE is a NASA infrared space telescope, initially launched to detect asteroids and other near-Earth objects. Over the course of its mission, it has also captured valuable data on various cosmic phenomena.
One of its major contributions is the observation of variable objects, whose brightness changes over time. This data, though secondary to NEOWISE's primary objective, is a goldmine for astronomers.
The mission has scanned the entire sky for over a decade, generating an unprecedented amount of information. Matteo Paz's analysis of this data revealed a vast number of previously unknown objects, significantly enriching our understanding of the Universe.