An alignment of galaxies creates this exceptional gravitational lens
Published by Cédric,
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: The Astrophysical Journal
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Article author: Cédric DEPOND
Source: The Astrophysical Journal
Other Languages: FR, DE, ES, PT
Follow us on Google News (click on ☆)
Astronomers recently highlighted this rare phenomenon in a study published in The Astrophysical Journal. Gravitational lenses are formed by the gravity of massive objects, such as galaxies. These objects distort space-time, allowing distant objects to be observed from a new perspective.
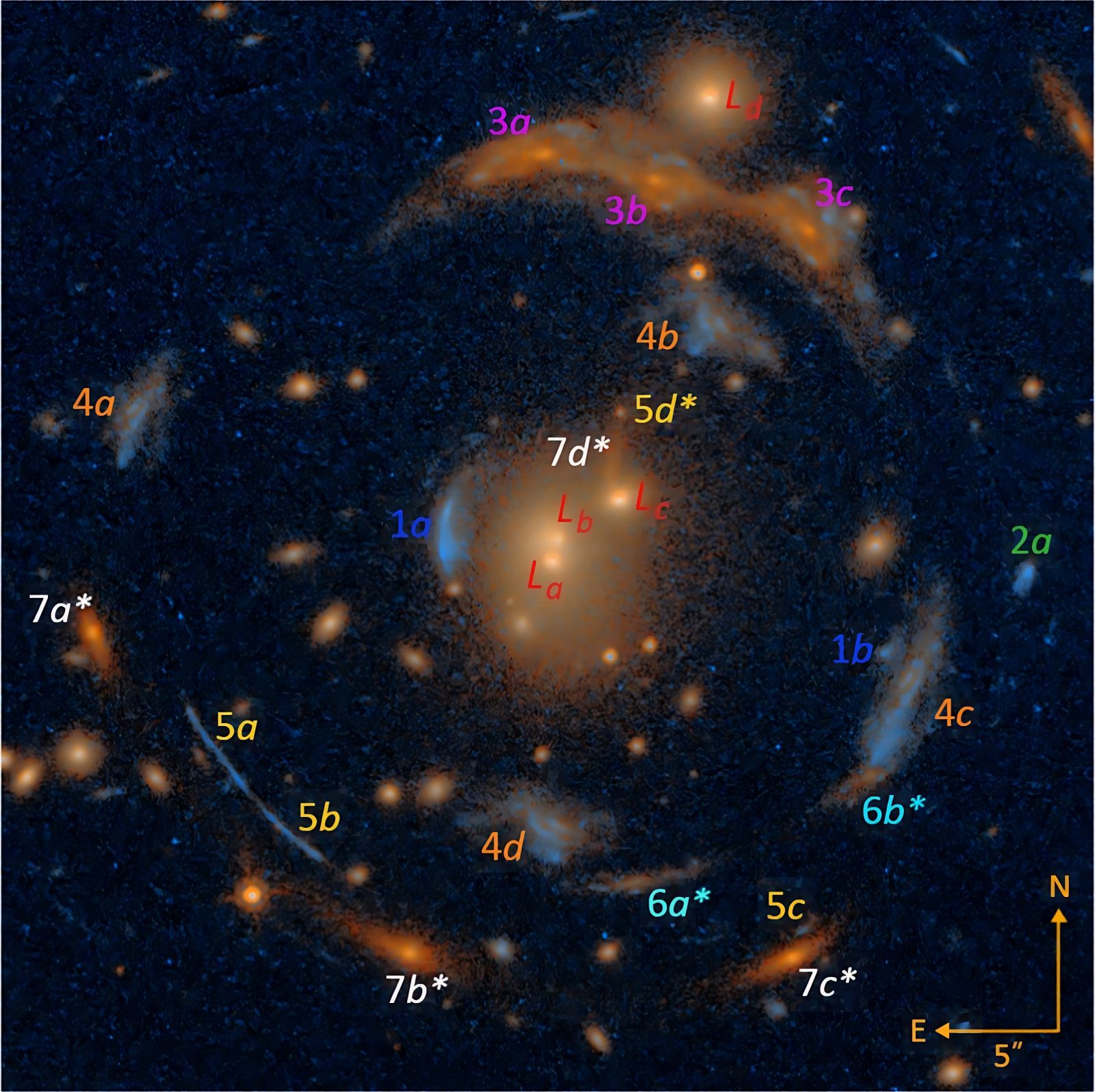
The designations 1x to 7x in the same color represent the same object, appearing multiple times in the same image due to lenticular distortion and amplification.
Four massive galaxies, located about five billion light-years from Earth, have thus acted as lenses, distorting the light of seven background galaxies, some of which are at impressive distances between 7 and 12 billion light-years.
This exceptional alignment is a cosmic stroke of luck, as David Schlegel, co-author of the study, explains. With a billion astrophysical objects examined, identifying this lens is a remarkable feat. It represents one unique object among a billion in the sky.
The carousel lens is more than a visual curiosity. It offers incredible potential for cosmological research, with in-depth studies on dark matter.
This lens allows observation of an “Einstein cross,” a configuration where four images of the same galaxy are visible at 90-degree angles. Such a formation helps understand the distribution of mass and the structure of the Universe.
Gravitational lenses help uncover the mysteries of dark matter, an invisible substance that constitutes a significant part of the Universe. By studying the curvature of light through these lenses, scientists can deduce the distribution of this elusive matter.
The extraordinary carousel lens provides an unprecedented opportunity to explore the depths of the Universe. By analyzing this data, astronomers will be able to test theories on dark matter and better understand the evolution of cosmic structures.
What is a gravitational lens?
A gravitational lens is a phenomenon that occurs when very massive objects, such as galaxies, curve the space around them with their gravity. If a distant galaxy lies behind these objects, the light from that galaxy is bent and magnified, similar to how a magnifying glass would behave. This allows astronomers to see distant galaxies they would otherwise not be able to observe.
In this case, it's not just one but four galaxies that formed a lens, allowing the observation of seven others that were perfectly aligned in the background!
The importance of gravitational lenses in the study of dark matter
Gravitational lenses play a key role in our understanding of dark matter, a still-mysterious substance that makes up much of the Universe. Although this matter is invisible and undetectable by conventional means, its gravitational influence manifests in the bending of light from distant galaxies.
By analyzing how this light is bent, astronomers can deduce the distribution and amount of dark matter present around galaxy clusters, thereby providing clues about its nature.
What is an Einstein cross?
An Einstein cross is a special formation that occurs when a gravitational lens distorts the light from a distant galaxy. This creates four distinct images of the same galaxy, which appear at 90-degree angles to each other, forming a shape resembling a cross.
This phenomenon helps astronomers study the mass distribution in the lens and better understand the properties of the Universe.